SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
WHAT IS SUBACROMIAL BURSAE?
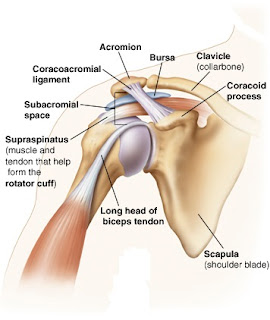
Subacromial bursa is
a sac like structure filled with fluid found in the shoulder joint. The subacromial
bursa separates the rotator cuff muscles, particularly the supraspinatus muscle
from the acromion process (a bony structure), the overlying coracoacromial
ligament and deltoid muscle.
The bursa provides a
smooth movement of the shoulder joint and reduce friction.
WHAT IS BURSITIS?
Bursitis is the
inflammation (irritation) of the bursa. The subacromial bursa is the most
commonly inflamed bursa in the shoulder joint. Inflammation of the subacromial
bursa becomes a cause of pain in performing activities and movements occurring
at shoulder joint. It leads to a restricted movement at the joint due to pain
while performing the motion. Hence, a restricted range of motion occurs.
WHAT CAUSES SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS?
·
Injury to the shoulder
·
Overuse of the shoulder joint
·
Calcium deposition
·
Rotator cuff tear
·
Muscle weakness
·
Impingement
·
Joint degeneration
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS?
· Repetitive injury to the shoulder joint:
The injury is caused due to repetitive
movements that occur at causing damage to the shoulder joint.
· Acute trauma
Any injury due to a fall, or direct hit to
the shoulder joint may lead to an inflammation in the
bursa.
· Overhead lifting movement
The bursa plays an important role in
supporting the rotator cuff muscles while performing overhead movements.
Frequent overhead movements of the arm leads to an overuse injury to the
shoulder joint and associated structures.
-A man hitting the nail with hammer on the wall
-An athlete who is doing an overhead throw of the ball
· Forceful pulling movement
The movement of frequent forceful pulling
leads to overuse and overexertion of the muscle, again
leading to damage to the
shoulder joint.
The movements with the forceful pulling
activities may include:
A man pulling heavy weight
A man pulling the rope in tug of war
SYMPTOMS OF THE SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
There
is a gradual onset of the symptoms
1. PAIN
Burning
pain in the shoulder radiating down the arm to elbow and wrist.
Pain
worsen on lying on the affected shoulder.
Increased
pain on performing movement including overhead activities like washing hair, combing
hair, reaching up to the cupboard or shelf.
Pain
while performing movements and at rest on the outer side of the shoulder.
2. RESTRICTED ROM
Pain
while performing activities at shoulder joint may lead to a reduced motion, the
person suffering from pain may not prefer to perform a movement which is
causing an increase in pain and worsening of the condition. Therefore, the
movements become restricted.
3. TENDERNESS
There
is a localized palpable tenderness on the anterior (front) and superior (upper)
part of the shoulder.
SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS IN DIABETICS AND TREATMENT
Shoulder
pain is one of the most commonly experienced pain hampering the day to day life
activities. When it comes to shoulder pain, the subacromial bursitis is
commonly encountered problem. A person having a history of type II Diabetes
when experiences a shoulder pain, the investigations often reveal a subacromial
bursitis. patient may complain of the pain on the outer side of the arm just
below the acromion on the shoulder. The pain is often dull and will occur more
while performing overhead activities. The most commonly affected movements at
the shoulder are the flexion (taking the arm up from front), abduction (taking
the arm up from side) and internal rotation. The inflamed bursa gets impinged
between the joint structures, the head of the humerus and the acromion process.
This pain can be relieved by attaining a position in which the two joint
surfaces moves apart for example in external rotation. Due to inability of healing
the damage and slow repair in diabetic patients, the situation gets worse. As the
damage occurring inside the body of the individual is not getting healed. The efficacy
of treatment and its results takes much longer time in diabetic patient than in
non-diabetics.
Physiotherapy
is the best possible treatment and also the preferred treatment in such cases.
At times
the result is not satisfactory in diabetic patients due to several
pathophysiological reasons going simultaneously in the body.
Corticosteroid
injections helps in such cases to a large extent (lidocaine + corticosteroids).
The aim here is to reduce pain and improve functions.
Therefore,
subacromial steroidal injections along with the physiotherapy management is the
best treatment to be followed.
PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC TREATMENT: (this treatment is followed for diabetics and non- diabetics as well)
ULTRASONIC therapy is given on the tender point: with intensity 1.5 W/Cm for 8 minutes.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): 15 minutes, electrodes on the shoulder and on the distal arm.
EXERCISES TO BE PERFORMED:
Table Slides
(Flexion): Patient starts with hand on a
table (facing the table) put a towel on the table and slide forward. Feel a stretch
under your arm. Do 10 repetitions. This exercise is modified for abduction as
well.
Table Slides
(Abduction): Patient starts with hand on
a table (by the side) put a towel on the table and slide forward. Feel a stretch
under your arm. Do 10 repetitions.
Upper Trap: Sit on a
table or chair and use the hand of the affected side to grip under the table, (this
stabilizes the shoulder). With the opposite hand, pull the head and tilt it to
opposite shoulder, feel a stretch in the upper trapezius muscle. Hold for 30
seconds and do 1-3 repetitions twice a day.
Open Book Stretch:
Place a rolled up towel on the couch between the two shoulder blades and lie
flat on your back. Keep your arms folded together over the top of your body.
Open your arms and then close. Repeat the procedure. Hold for 30 seconds and do
1-3 repetitions twice a day.
Wall Push Ups: stand
in front of the wall and bend your elbows and move toward the wall. Then extend
your arms and push the wall as far away as possible without your palms leaving
the wall. Repeat 10 times.
Rowing (using a
theraband): Sit on a chair. Tie a theraband on a door or a pole, around chest
level. Pull the theraband backwards (this pulls shoulder blades together). Do 10
repetitions.
RANGE OF MOTION EXERCISES:
Shoulder wheel
Finger ladder
Shoulder pulley
SHOULDER STRETCH:
Biceps stretch
Triceps stretch
Pectoral stretch
Trapezius stretch
TO PREVENT SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
Avoid carrying heavy
loads.
Avoid too much of
overhead activities.
Do not pull heavy
objects.



















Comments