SELFIE ELBOW
As you all must have read my previous article which
was based on the damage to our neck because of the excessive use of technology,
I am adding one more tech-induced ailment to my list which is the ‘SELFIE ELBOW’.
Yes, you got it right. As the name suggests, ‘selfie elbow’ is also a modern
tech-induced ailment which is affecting a lot of selfie lovers these days. People
like me and you, who do not have any sports background or record of being
indulged in a sport like tennis or golf which requires repeated use of extended
arm and repetitive jerk on the elbow are having problems which resembles the
symptoms of the same. Each time you click a picture, you put yourself in a
position where your arm is fully extended, or sometimes the elbow is a little
bent and the position is maintain until you get the picture of your choice and
you are keeping a firm grip on your phone to keep holding it and to hit a click
just when you get that ‘right frame’. It can be counted as one of the
repetitive strain injuries. So taking correct selfies has now become a pain in
the elbow!
Unknowingly, ‘selfie elbow’ has become a real matter of
concern now. What effects are being caused on the body due to this habit, let’s
take a closer look at the condition.
A CLOSER LOOK AT THE CONDITION:
Recently, the award winning US journalist and NBC’s Today
show host Hoda Kotb, who is famous for her social media picture sharing on Instagram
has been diagnosed with a condition of ‘selfie elbow’, however, the condition
is not so commonly spread till now but the chances are there for a speedy
travel of this technology based disorder throughout the world. The common
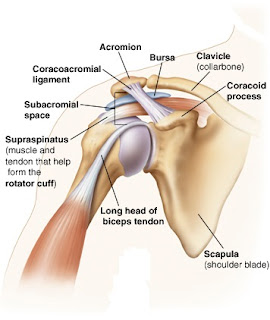
joints involved in the condition are the shoulder joint, elbow joint and the
wrist joint simultaneously helping the hand to attain a perfect frame for the picture.
But, most of the strain is caused in the elbow. This is because you extend
(straightened) your elbow in an extremely strained position. Or sometimes you
keep it a bit flexed (bent). The posture causes repetitive strain and overuse
of the surrounding structures at the elbow which is the target joint. Most of
the work is done by elbow in this position but a grip maintained at the hand
holding the phone is worsening the condition. Due to repetitive motion, there
are microruptures around the elbow and the tendon running through the elbow
joint is inflamed causing pain and discomfort. The condition may not necessarily
be an acute injury to the tendon but this may also be a degenerative changes
that has been occurring around the structures of the elbow not only because of
your habit of clicking selfies but it may also be any type of repeated movement
you are performing at your home while cooking or gardening or playing tennis or
golf. Hence, this may be a re-occurrence of a condition that was unknowingly
persisting in your body. There can be swelling observed around the elbow joint’s
extensor origin as well, because most of the work in this position is carried
out by the extensor compartment of the muscles in the elbow and the strain is
caused to the tendinous muscle attachments. Once the condition has occurred,
minimum amount of load or work carried out by the elbow will cause a lot of
pain, this is because the muscles of the elbow has already weakened. And the
damage has already taken place which has yet not been cured. Eventually, there
occurs a loss of function.
ANATOMY OF THE ELBOW JOINT:
Elbow joint is a hinge joint, formed between the humerus in
the upper arm and radius and ulna in the lower arm.
There are seven major muscles which helps to perform various
movements at the elbow joint:
THE FLEXOR GROUP: (3 MUSCLES)
·
Biceps brachii: flexion of the elbow i.e.
bringing the upper and the lower arm together and supination i.e. turning the
palm anteriorly.
·
Brachialis: this is the primary flexor muscle at
the elbow joint.
·
Brachioradialis: flexion at the elbow joint and
is found mainly in the forearm, enables flexion at the elbow in a mid-prone
position.
THE EXTENSOR GROUP: (2 MUSCLES)
·
Triceps brachii: runs posteriorly to the arm and
enables extension at the elbow joint i.e moving the upper and the lower arm
away from each other while increasing the angle at the elbow joint.
·
Anconeus: it is a small muscle at the elbow
joint which contributes in the elbow extension along with the tricep.
THE ROTATORS: (2 MUSCLES)
·
Pronator teres: runs obliquely in the elbow
joint and performs the action of pronation of the arm i.e. turning the arm
posteriorly
·
Supinator: the muscle enabales the action of
supination at the elbow joint i.e. turning the arm anteriorly.
There are a few more muscles in the forearm that crosses the elbow joint
to move the wrist and the fingers.
THE FLEXOR GROUP:
·
Flexor carpi radialis
·
Flexor carpi ulnaris
·
Palmaris longus
·
Flexor digitorum profundus
All these muscles originate from the medial epicondyle of the elbow and
helps in the making a fist by the fingers (contraction of the palm) and flexion
(bending) at the wrist joint.
THE EXTENSOR GROUP:
·
Extensor carpi radialis longus
·
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
·
Extensor digitorum
All these muscles originates from the lateral epicondyle of the elbow
joint and helps to open the fist and extend the wrist.
THE C6 ROOT MOTOR GROUP AND THE C7 ROOT MOTOR GROUP ARE THE MAJORLY
INVOLVED MUSCLE GROUPS AND MOVEMENTS INVOLVED IN SLEFIE ELBOW:
C6 MYOTOMES:
Ø
SHOULDER ADDUCTION
Ø
ELBOW FLEXION
Ø
FOREARM SUPINATION
C7 MYOTOMES:
Ø
ELBOW EXTENSION
Ø
FOREARM PRONATION
Ø
WRIST EXTENSION
Ø
THUMB, FINGER EXTENSION
SYMPTOMS OF THE SELFIE ELBOW:
·
Burning pain around elbow
·
Pain while performing actions at elbow and wrist
·
Limitation of motion at elbow and wrist
·
Stiffness in the arm (more in morning)
·
Muscle fatigue
HOW TO GET RID OF THE CONDITION?
·
REST:
Give rest to your arm. Avoid clicking a lot of selfies. Use a selfie
stick (not too much), use both hands while holding your phone during a click,
or switch hands to avoid overuse.
·
ICE:
To reduce inflammatory symptoms in the area. Ice is only prescribed when
there is a visible and palpable swelling around the area. But as I mentioned
the condition may be a chronic one as well, there, ice won’t work.
So here, it becomes the priority to diagnose first, whether the condition
is an acute or a chronic one.
·
MEDICATION:
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) to reduce the inflammation
and its associated symptoms i.e. pain, swelling, warmth, redness.
ANALGESICS to reduce pain.
·
PHYSIOTHERAPY:
Perform full range active movement of the elbow.
 |
| flexion and extension |
 |
| supination and pronation |
Stretch the muscles. The common stretches are:
Biceps stretch:
Triceps stretch:
Strengthen the weakened muscles around the elbow joint:
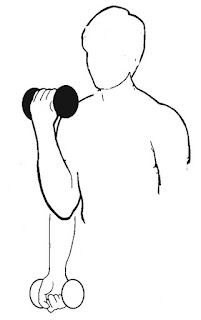
Add resistance to the arm in the form of weight cuffs, dumbbells, therabands,
medicine balls and perform the following actions:
-elbow extension and flexion:
Wrist flexion:
Wrist extension:
·
BRACES AND SUPPORT:
Use elbow caps to support the elbow joint while in pain.
Braces
should be used only for a short span of time, as soon as you begin to observe
improvement in the condition you should stop using braces, as it might support
the elbow while in pain but simultaneously it causes the muscles to forget
their action enhancing the muscle weakness and also it promotes immobility to
some extent.










Comments